AWS Session Manager
This feature has been removed! NETworkManager 2025.10.18.0 will be the last version to support the AWS Session Manager feature.
The AWS Session Manager Plugin is not actively maintained and contains several bugs (e.g. German / Spain keyboard layout issues). The current code base was also difficult to maintain and extend, and I currently have no test environment.
You can still use AWS Session Manager within NETworkManager with the PowerShell feature by using the aws ssm start-session --target <instance-id> command.
With AWS (Systems Manager) Session Manager, you can connect to and manage an EC2 instance without opening inbound ports, running a bastion host, or managing SSH keys. The integration of AWS Session Manager with NETworkManger supports tabs and profiles for hosts. The connection can be established via a profile (double-click, Enter key or right-click Connect) or directly via the connection dialog. You can also synchronize your EC2 instances from AWS. To connect to the instances a PowerShell console is used with the AWS CLI and the AWS Session Manager plugin. The connection to the instances is established via the following command:
aws ssm start-session --target <instance-id>
Here you can find more information about AWS Systems Manager and the documentation for AWS Systems Manager Session Manager. You need to setup you AWS account to use AWS Systems Manager Session Manager. See Prerequisites for more details.
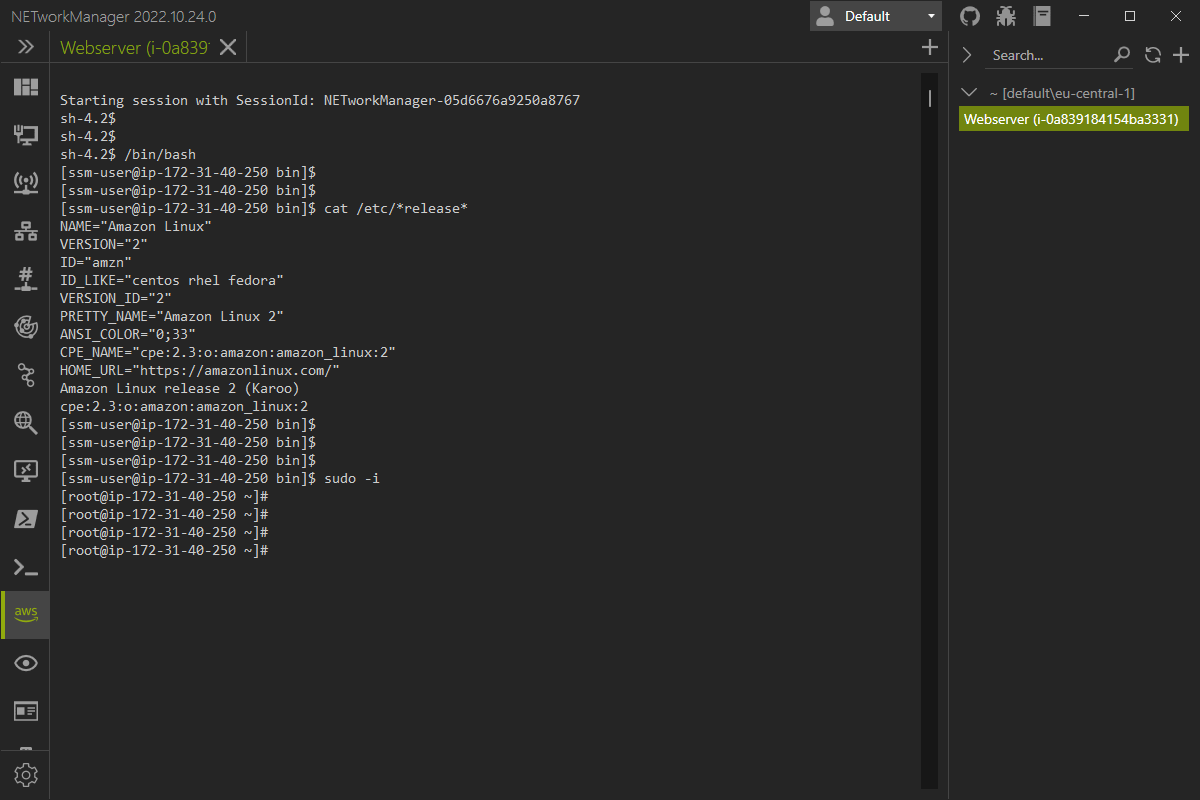
Right-click on the tab will open the context menu with the following options:
- Reconnect - Restart the PowerShell console and reconnect to the AWS instance.
- Resize - Resize the PowerShell console to the current view size (if connected).
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites must be met to use AWS Systems Manager Session Manager.
- Setup AWS CLI & Session Manager plugin
- Setup AWS Systems Manager Session Manager
- Setup AWS IAM user to sync and connect
- Verify the connection
Setup AWS CLI & Session Manager plugin
The AWS CLI and AWS Session Manager plugin is required on your computer to run the aws ssm start-session command. You can download them here:
- AWS CLI (direct link Windows installer)
- AWS Session Manager plugin (direct link Windows installer)
See the AWS documentation for installation instructions.
Setup AWS Systems Manager Session Manager
To connect to the instances, the AWS Systems Manager Session Manager must be configured in AWS. See their documentation for instructions on how to set up the Session Manager.
Below you will find an example configuration:
Example SSM-SessionManagerRunShell document
This is an example of the AWS Systems Manager Session Manager configuration and may not be suitable for a production environment.
Create a JOSN file with the name SessionManagerRunShell.json and the following content:
{
"schemaVersion": "1.0",
"description": "Document to hold regional settings for Session Manager",
"sessionType": "Standard_Stream",
"inputs": {
"s3BucketName": "<S3_BUCKET>",
"s3KeyPrefix": "<S3_BUCKET_PREFIX>",
"s3EncryptionEnabled": true,
"cloudWatchLogGroupName": "<CLOUDWATCH_GROUPNAME>",
"cloudWatchEncryptionEnabled": true,
"cloudWatchStreamingEnabled": false,
"kmsKeyId": "<KMS_KEY_ARN>",
"runAsEnabled": true,
"runAsDefaultUser": "<SSM_RUNASUSER>",
"idleSessionTimeout": "20",
"maxSessionDuration": "60",
"shellProfile": {
"windows": "<LINUX_COMMANDS>",
"linux": "<WINDOWS_COMMANDS>"
}
}
}
Create the document in AWS SSM via AWS CLI:
aws ssm create-document \
--name SSM-SessionManagerRunShell \
--content "file://SessionManagerRunShell.json" \
--document-type "Session" \
--document-format JSON
Example IAM role / instance profile
This is an example of an IAM role/instance profile that allows access from AWS Systems Manager Session Manager to the instance and may not be suitable for a production environment.
Create a new IAM role/instance profile with the following content:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
Add an (inline) policy to the role with the following content:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ssmmessages:CreateControlChannel",
"ssmmessages:CreateDataChannel",
"ssmmessages:OpenControlChannel",
"ssmmessages:OpenDataChannel",
"ssm:UpdateInstanceInformation"
],
"Resource": "*"
} /*,
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents",
"logs:DescribeLogGroups",
"logs:DescribeLogStreams"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<S3_BUCKET>/<S3_BUCKET_PREFIX>/*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetEncryptionConfiguration"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"kms:Decrypt"
],
"Resource": "<KMS_KEY_ARN>"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "kms:GenerateDataKey",
"Resource": "*"
}*/
]
}
Setup AWS IAM user to sync and connect
For the snychronization of the EC2 instances and to connect to them via AWS Systems Manager Session Manager, a separate user with minimal privileges should be set up. For the synchronization from AWS EC2 the permissions ec2:DescribeInstances and ec2:DescribeInstanceStatus are required. Additionally, the user must be able to connect to the instances via AWS Systems Manager Session Manager. Below are examples of both policies:
Example sync policy
This is an example of an IAM user policy to synchronize instances of AWS EC2 for NETworkManager.
Add an (inline) policy to the user with the following content:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowNETworkManagerSync",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["ec2:DescribeInstances", "ec2:DescribeInstanceStatus"],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Example connect policy
This is an example of an IAM user policy that allows access to EC2 instances through AWS Systems Manager Session Manager and may not be suitable for a production environment.
Add an (inline) policy to the user with the following content:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["ssm:StartSession"],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:ec2:<AWS_REGION>:<ACCOUNT_ID>:instance/*",
"arn:aws:ssm:<AWS_REGION>:<ACCOUNT_ID>:document/SSM-SessionManagerRunShell"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ssm:DescribeSessions",
"ssm:GetConnectionStatus",
"ssm:DescribeInstanceProperties",
"ec2:DescribeInstances"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["ssm:TerminateSession", "ssm:ResumeSession"],
"Resource": ["arn:aws:ssm:*:*:session/${aws:username}-*"]
} /*,
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["kms:GenerateDataKey"],
"Resource": "<KMS_KEY_ARN>"
}*/
]
}
API keys must be generated for the user and the AWS CLI must be configured (See aws configure and ~\.aws\credentials file for more details).
Sensitive data like the API keys are stored in plain text in the file ~\.aws\credentials!
Verify the connection
You can verify the connection to the EC2 instance through AWS Systems Manager Session Manager by opening a PowerShell and connecting to the instance through AWS CLI:
aws ssm start-session --target instance-id <instance-id>
Connect
Instance ID
ID of the AWS EC2 instance.
Type: String
Default: Empty
Example: i-0123456789abcdef0
Profile
AWS CLI profile which will be used to connect.
Type: String
Default: Empty or from settings
Example: dev
If not set, the AWS CLI default settings are used!
Region
AWS region where the instance is located.
Type: String
Default: Empty or from settings
Example: eu-central-1
If not set, the AWS CLI default settings are used!
Profile
Instance ID
ID of the AWS EC2 instance.
Type: String
Default: Empty
Example: i-0123456789abcdef0
Profile
AWS CLI profile which will be used to connect.
Type: String
Default: Empty
Example: dev
Region
AWS region where the instance is located.
Type: String
Default: Empty
Example: eu-central-1
Group
Profile
AWS CLI profile which will be used to connect.
Type: String
Default: Empty
Example: dev
Region
AWS region where the instance is located.
Type: String
Default: Empty
Example: eu-central-1
Settings
Synchronize EC2 instances from AWS
If enabled, EC2 instances are synced from AWS. In addition, the profiles and regions to be synchronized must be configured.
Type: Boolean
Default: Disabled
Profiles and regions to synchronize
Here you can specify a combination of AWS CLI profile and AWS region from where the EC2 instances should be synchronized. Multiple AWS accounts and regions are supported.
Type: List<NETworkManager.Models.AWS.AWSProfileInfo>
| Property | Type |
|---|---|
Enabled | Boolean |
Profile | String |
Region | String |
Default:
| Enabled | Profile | Region |
|---|---|---|
Disabled | default | eu-central-1 |
Disabled | default | us-east-1 |
Example:
| Enabled | Profile | Region |
|---|---|---|
Disabled | dev | eu-central-1 |
Disabled | dev | us-east-1 |
Disabled | prod | eu-central-1 |
Disabled | prod | us-east-1 |
Right-click on a selected profile to edit or delete it.
You can also use the Hotkeys F2 (edit) or Del (delete) on a selected profile.
Only enabled profiles are synchronized and Synchronize EC2 instances from AWS must be enabled!
Synchronize only running EC2 instances from AWS
If enabled, only EC2 instances are synchronized where the instance state is running.
Type: Boolean
Default: Enabled
Profile
AWS CLI profile which will be used to connect for manually added profiles.
Type: String
Default: Empty
Example: dev
If not set, the AWS CLI default settings are used!
Region
AWS region where the instance is located for manually added profiles.
Type: String
Default: Empty
Example: eu-central-1
If not set, the AWS CLI default settings are used!
File path
Path to the PowerShell console where the AWS CLI is available.
Type: String
Default: C:\Program Files\PowerShell\7\pwsh.exe, C:\Program Files (x86)\PowerShell\7\pwsh.exe or C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
Example:
C:\path\to\PowerShell.exeC:\path\to\pwsh.exe
The Configure button opens the PowerShell console to configure it.